|
WELDING NECK FLANGE
This group of flanges is designed with a hub on the backside
tapering to a diameter that will match the pipe to which it
will be welded. The lighter the pipe is, the larger the
bore, conversely, the heavier the pipe, the small the bore.
These flanges are bored to match the inside diameter of the
mating pipe so there will be no restriction of product flow.
This prevents turbulence at the joint and reduces erosion.
Welding neck flanges are preferred for use in severe service
applications involving high pressure, cold or hot
temperatures. They also provide excellent stress
distribution through the tapered hub and are easily
radiographer for flaw detection.
|
 |
| |
|
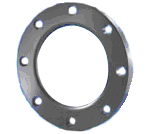
LAP JOINT FLANGE
Used in conjunction with a "Lap Joint Stub End," these
flanges are nearly identical to a slip-on flange with the
exception of a radius at the intersection of the flange face
and the bore to accommodate the flanged portion of the stub
end. These flanges are used in applications where the joint
must be frequently disassembled for cleaning or where there
is a need to facilitate bolt alignment.
|
 |
| |
|
|
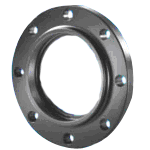
SOCKET WELDING FLANGE
This flange is similar to slip-on flange, except they a bore
and a counter bore. The counter bore is slightly larger than
the Outer Diameter of the matching pipe, allowing the pipe
to be inserted. A restriction is built into the bottom of
the bore, which acts as a shoulder for the pipe to rest on,
and has the same ID of matching pipe. The flange is then
attached to the pipe by a fillet weld at the hub. The
shoulder made by the difference between the bore and counter
bore is the same width as the wall of the pipe, thereby
providing for an unrestricted flow of product through the
connection. These flanges were initially developed for use
in small diameter, high- pressure lines. Internally welded
socket type flanges are typically used in chemical
processes, hydraulic lines and steam distribution lines. |
 |
| |
|
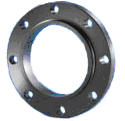
SLIP-ON FLANGE
A Slip-on Flange is bored slightly larger than the outer
Diameter of the matching pipe. The pipe slips into the
flange prior to welding both inside and outside to prevent
leaks. These flanges are attached to the pipe by fillet
welding at the hub and at the end of the pipe inside the
flange.
|
 |
| |
|
THREADED FLANGE
Threaded flanges are threaded in the bore to match an
external thread on the pipe. The threads are tapered to
create a seal between the flange and pipe as the tapers
approach the same diameter. These flanges are normally
designed for low pressure, non-cyclic applications. They are
also used in applications where welding is hazardous.
|
 |
| |
|
BLIND
FLANGES
These flanges are manufactured without a bore and used as
closures or seals for the ends of piping systems. They are
also used to provide access covers for pressure vessels.
Blind flanges are provided with or without a hub, depending
on customer requirements. Under pressure and bolt loading,
the blind flange is subjected to more stresses than any
other flange type. However, the maximum stresses are bending
stresses at the center and are easily absorbed by the
flange. |
 |
| |
|
ORIFICE
FLANGES
Designed for flow metering systems. Two of these flanges
with bolts and jack screws are called an "orifice flange
union" and are used in conjunction with an "orifice plate."
The orifice plate is a separate commodity and is not sold as
a part of the flange assembly. Each flange is provided with
a pair of pressure taps for measurement of pressure drop in
the flow through the orifice plate. The taps are precisely
located with respect to the orifice plate. Orifice flanges
may be provided in one of three types of flanges: Welding
Neck, Slip-On and Threaded. |
 |
| |
|
PLATE
FLANGES
Plate flanges are a widely accepted and cost effective
alternative to forged or cast flanges in low pressure
applications. Over the years, a number of standards have
been applied to the production of steel plate flanges.
Our plate flange product line includes standard and non
standard flanges from 31/2" to 200" in diameter produced to
all applicable standards.
|
 |
| |
|
Flange Material |
Flange Specification |
|
1.
Carbon steel (ASTM A105)
2.
Stainless Steel
3. Alloy
Steel
4. Duplex
Steel
5. Super
Duplex Steel
6. Galvanized
Steel
7. Low
Temperature Carbon Steel
8. High
Yield Sustenite
9. Others
as specified by customer |
1.
ASTM
2.
ASME
3. JIS
4. MSS
5. API
6. DIN
7. British
8. ISS
9. Many
other specifications and also as per customerís
drawing and specification |
|











